how long does it take for enlarged prostate to go down
New Treatment Option Available For Men Suffering From ... for Beginners
A person might need other treatments in addition to medication. Treatment might involve a minimally invasive procedure that a physician carries out through a catheter, surgical treatment to eliminate tissue from the prostate, or way of life modifications. types.
The condition effects about 50% of guys in between the ages of 51 and 60. For males 80 and older, the frequency of BPH is around 90%, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Gastrointestinal and Kidney Diseases. While BPH can have major complications, it is not a cancer and is generally linked to a man's aging process.
If left untreated, BPH can cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney issues. Although numerous males with BPH have no signs, others show signs, referred to as lower urinary system signs. They can range from mild and hardly visible to major, however the quantity of prostate enlargement is not straight related to the severity of the symptoms.
4 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius), chills or body pains - urinary tract infections. He feels pain in his lower back, simply listed below the chest, that is not associated with an injury or physical effort. There is blood or pus in his urine or semen. A doctor can diagnose BPH, by asking questions about the signs and by doing a physical examination.
Some Ideas on New Treatment Option Available For Men Suffering From ... You Should Know
Sometimes, a prostate-specific antigen test is done to assist eliminate prostate cancer - enlarged prostate. Although prostate cancer and BPH are not related, they can have a few of the very same symptoms. If signs are mild to moderate and aren't too annoying, house treatment might be all that is required to keep them under control.
Because BPH can not be cured, the treatment concentrates on minimizing the symptoms (fruit). The treatment is based on how extreme the symptoms are, just how much they bother the patient and whether there are issues. The more annoying the signs are, the more aggressive treatment should be. Issues, such as continuous failure to urinate, urinary system infections, bladder stones, kidney damage or continuous blood in the urine, ought to be treated with surgical treatment.
Articles from Restorative Advances in Urology are supplied here thanks to
In the 1960's, alpha blocker medications, which were at first developed and utilized for the function relaxing muscles in the prostate gland, have actually slowly become more accessible and specific for the prostate tissue. Additional medications have actually likewise been developed and enhanced, but among the newest is a day-to-day dosage of tadalafil.
The 30-Second Trick For Treatment For Enlarged Prostate - Mayo Clinic Health System
In addition to this, other medications for urinary signs, such as mirabegron, can likewise be used to enhance bladder storage and relaxation and ease the urinary signs of seriousness and frequency that can sometimes co-exist or be an outcome of prostate enhancement. Among the earliest surgical treatment techniques, the TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate gland) treatment, is still carried out today.

These instruments can then be utilized to shave down the interior of the prostate gland. The latest treatment choices all construct upon this principle of removing and/or alleviating the blockage that is blocking the circulation of urine - bladder.
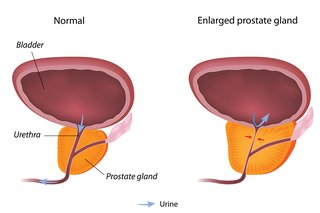
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) happens when a male's prostate swells, which in turn puts pressure on the urethra and prevents urine from having the ability to pass (turp). BPH is a common occurrence seen in guys as they age, impacting about 50% of men in between the ages of 51 and 60, and 90% of guys older than 80.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that occurs when the prostate and surrounding tissues expand. Normally, a male's prostate is approximately the size of a walnut or golf ball, nevertheless, it has the prospective to grow up to the size of an orange as the gland grows.
A Biased View of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Bph): Symptoms & Treatment
These symptoms can include: Weak or irregular urine stream Straining to urinate Beginning and stopping throughout urination Regular urge to urinate throughout the night Having to urinate once again shortly after urination If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to contact a urologist as quickly as possible (caffeine).
Continue reading for more information about the finest treatment for enlarged prostate. resection. Rezm water therapy is an excellent alternative to offer enduring relief for those who do not wish to treat BPH with medication or intrusive surgical treatment. This is a non-surgical treatment that uses the power of water, vapor, or steam, to get rid of excess prostate tissue that is pressing against the urethra, triggering lower urinary tract symptoms.
Having BPH can imply regular journeys to the bathroom and even interrupted sleep. The best advantage of Rezm water treatment is how it works to eliminate discouraging BPH signs that otherwise may still be present (benign prostatic hyperplasia). Rezm water therapy does not need uncomfortable surgical treatment or medication, and is minimally invasive. Furthermore, It'll provide you the opportunity to have a strong steady stream without having to take prostate medications or recuperate from a surgery.
The main objective of the Uro, Lift system is to alleviate symptoms of BPH so clients can resume their day-to-day activities without having to stress about constantly going to the restroom (life). Uro, Lift is the only transurethral BPH treatment that does not need ongoing medication, cutting, heating, or removal of the prostate tissue.
The Only Guide for Enlarged Prostate - Stanford Health Care
Both treatments will fix your enlarged prostate symptoms and offer you peace of mind. If neither of these choices appear right for you, there are alternative techniques to treat BPH, such as medications or surgical treatment. Rezm and Uro, Lift are the finest treatment for enlarged prostate, they aren't the only techniques offered to you.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, a noncancerous augmentation of the prostate gland, is the most common benign growth found in guys. As holds true for prostate cancer, BPH takes place regularly in the West than in Eastern countries, such as Japan and China, and it may be more common among black people.
BPH produces symptoms by obstructing the flow of urine through the urethra. Symptoms associated with BPH are present in about one in four guys by age 55, and in half of 75-year-old men. Nevertheless, treatment is just required if symptoms become irritating. health problems. By age 80, some 20% to 30% of men experience BPH symptoms extreme enough to require treatment.
BPH symptoms can be divided into those triggered straight by urethral blockage and those due to secondary modifications in the bladder. Difficulty beginning to urinate despite pushing and straining A weak stream of urine; numerous interruptions in the stream Dribbling at the end of urination An unexpected strong desire to urinate (urgency) Frequent urination The feeling that the bladder is not empty after urination is completed Frequent awakening in the evening to urinate (nocturia) As the bladder ends up being more conscious maintained urine, a guy might end up being incontinent (not able to control the bladder, causing bed wetting in the evening or failure to react rapidly enough to urinary urgency) (bipolar).
The Definitive Guide for What Treatments Are Available For An Enlarged Prostate?
Blood in the urine (hematuria) might declare BPH, but most men with BPH do not have hematuria. The American Urological Association (AUA) Sign Index offers an objective assessment of BPH symptoms that assists figure out treatment. surgery. This index can not be used for diagnosis, considering that other illness can cause signs similar to those of BPH.
Strictures can arise from urethral damage brought on by previous trauma, instrumentation (for instance, catheter insertion) or an infection such as gonorrhea. Bladder cancer is suspected if there is a history of blood in the urine. Pain in the penis or bladder area may indicate bladder stones, infections, or inflammation or compression of the pudendal nerve - way.
A thorough case history should consist of questions about any worsening of urinary symptoms when taking cold or sinus drugs, and previous urinary tract infections or prostatitis (swelling of the prostate, which might cause pain in the lower back and the location in between the scrotum and rectum, and chills, fever and general despair) - purposes.
Symptoms, in addition to objective measurements of urethral blockage, can stay stable for several years and might even improve in time for as lots of as one-third of guys, according to some research studies. md. In a study from the Mayo Center, urinary signs did not aggravate over a 3. 5-year period in 73% of guys with moderate BPH.
How 6 Effective Natural Remedies For Enlarged Prostate - Imaware™ can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.
In basic, no treatment is indicated in those who have just a few symptoms and are not bothered by them. Intervention typically surgical is needed in the following situations: Insufficient bladder clearing resulting in damage to the kidneys Total failure to urinate after severe urinary retention Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder Bladder stones Contaminated recurring urine Reoccurring extreme hematuria Symptoms that problem the patient enough to decrease his quality of life Treatment choices are harder for guys with moderate symptoms (alpha blockers).
Each specific must determine whether the signs disrupt his life enough to benefit treatment. When picking a treatment, both patient and physician need to balance the efficiency of various types of treatment versus their adverse effects and expenses - turp procedure. Currently, the main choices to attend to BPH are: Watchful waiting Medication Surgical treatment (prostatic urethral lift, transurethral resection of the prostate, photovaporization of the prostate, open prostatectomy) If medications are ineffective in a male who is not able to endure the rigors of surgery, urethral blockage and incontinence may be handled by periodic catheterization or an indwelling Foley catheter (which has an inflated balloon at the end to hold it in place in the bladder).
Because the progress and problems of BPH are unpredictable, a method of careful waiting no immediate treatment is tried is finest for those with very little symptoms that are not especially bothersome. Doctor sees are required about when each year to review the development of symptoms, carry out an evaluation and do a few simple laboratory tests.
In some men, finasteride can alleviate BPH symptoms, increase urinary flow rate and shrink the prostate, though it needs to be used indefinitely to avoid recurrence of symptoms, and it might take as long as 6 months to attain optimum benefits. In a research study of its security and effectiveness, two-thirds of the guys taking finasteride experienced: A minimum of a 20% decline in prostate size (just about half achieved this level of reduction by the one-year mark) Enhanced urinary circulation for about one-third of patients Some relief of signs for two-thirds of clients A research study released in 2015 recommends that finasteride might be finest matched for guys with reasonably large prostate glands.
The 7-Minute Rule for What Is The Best Treatment For Enlarged Prostate?
Finasteride can reduce PSA levels by about 50%, but it is not thought to limit the utility of PSA as a screening test for prostate cancer. The fall in PSA levels, and any adverse effects on sexual function, vanish when finasteride usage is stopped - surgery. To get the benefits of finasteride for BPH without jeopardizing the detection of early prostate cancer, men ought to have a PSA test prior to beginning finasteride treatment.
If a man is already on finasteride and no standard PSA level was acquired, the outcomes of an existing PSA test should be multiplied by 2 to approximate the true PSA level. A fall in PSA of less than 50% after a year of finasteride treatment recommends either that the drug is not being taken or that prostate cancer may be present.
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, such as Cialis, are frequently used for impotence, but when utilized daily, they also can relax the smooth muscle of the prostate and overactivity of the bladder muscle. Studies taking a look at the impact of day-to-day Cialis use compared to placebo showed a decrease in International Prostate Sign Rating by four to 5 points, and Cialis was superior to placebo in minimizing urinary frequency, seriousness and urinary incontinence episodes. prostate enlargement.
With thermal therapies, several treatment sessions may be required, and the majority of men need more treatment for BPH symptoms within 5 years after their preliminary thermal treatment. This procedure was initially used in the U.S. in the early 1970s. Like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), it is done with an instrument that is gone through the urethra.
how long does it take for enlarged prostate to go down